Roller screen is a widely used pre-treatment screening equipment in industries such as mining, coal, electricity, and building materials. It is known for its sturdy structure, large processing capacity, and particularly good at handling sticky and wet materials. Below, we will help you sort out the common knowledge about roller screens from five aspects: working principle, main functions, production capacity, application field, and applicable materials, so that as your reference when purchasing equipment and evaluating project requirements.

Working Principle
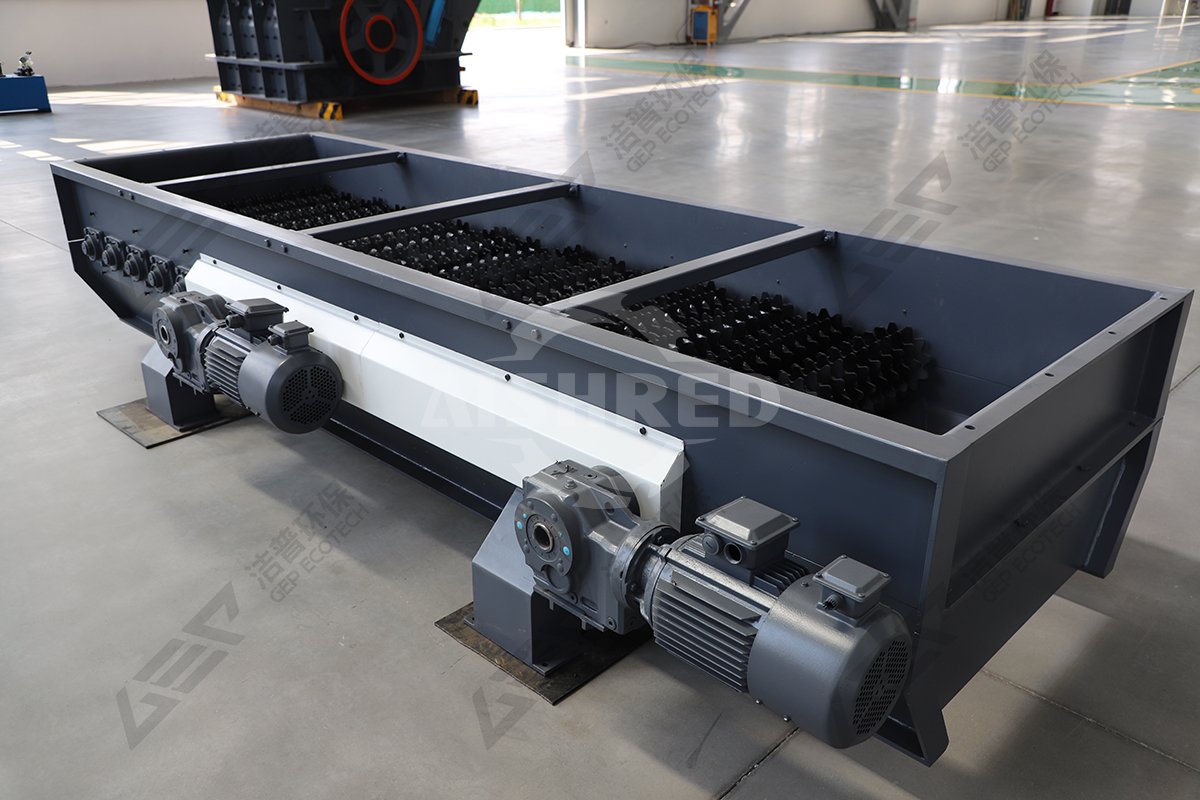
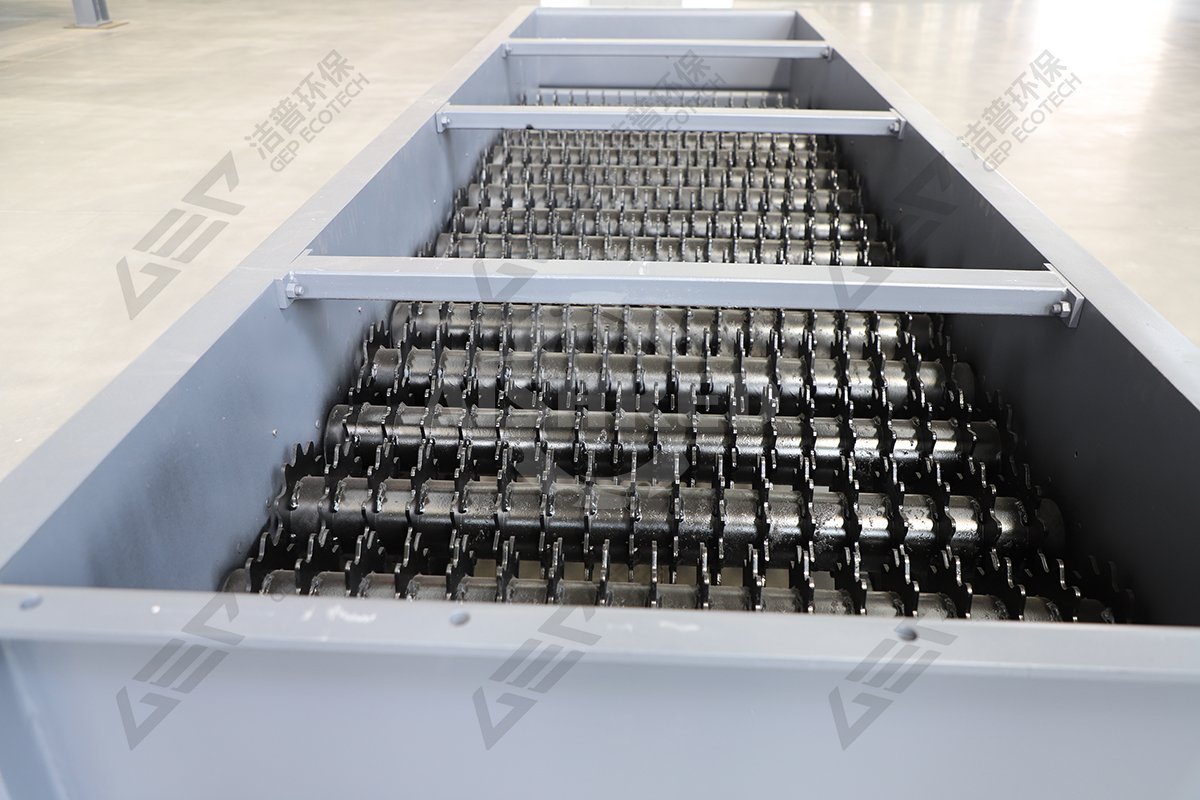
Structural composition: The roller screen is mainly composed of multiple parallel arranged screen shafts, screen discs (or screens) installed on the screen shafts, transmission devices (motors, reducers), boxes, and brackets.
Movement mode: Each sieve shaft is driven by a transmission device to rotate in the same direction. The installation method between the sieve shafts allows the sieve plates on adjacent sieve shafts to be arranged in a staggered manner, forming a sieve surface similar to a "stepped" shape.
Screening process:
The material falls into the sieve box from the feeding port and onto the first rotating sieve shaft.
When the sieve disc (or comb teeth) on the sieve shaft rotates, it "grabs" and "stirs" the material, while conveying it forward.
During this process, small particles (undersized material) smaller than the gap between the sieve plates will fall through the gap and achieve sieving.
The block shaped materials (sieved materials) larger than the gap are driven by the sieve plate and transported step by step to the discharge end along the inclined direction of the sieve surface or by the "step" effect of the installation angle of the sieve shaft.
Key point: Its screening does not rely on vibration, but on the rotational motion of the sieve plate to forcibly transport and stir materials, thus it has good adaptability to sticky and wet materials that are prone to clogging.
Main Functions
Preprocessing and Grading: Classify raw materials according to particle size, such as dividing raw coal into lump coal and fine coal, or dividing ore into large blocks and powder.
Removal of impurities and media: In coal preparation plants, it is used to remove suspensions used as sorting media (such as magnetite powder) from heavy media coal preparation systems.
Protecting downstream equipment: As a front-end screening device for crushers, feeders, and other equipment, it pre screens out fine materials that do not need to be crushed or removes large debris, improving system efficiency and protecting critical equipment.
Uniform feeding: Capable of uniformly conveying and distributing materials to downstream equipment or belt conveyors.
Production Capacity
The production capacity of a roller screen is a variable that is influenced by multiple factors, typically ranging from tens to thousands of tons per hour. It depends on:
Screen size (width and length): The wider and longer the screen, the greater the processing capacity.
Screen gap size: The larger the screen gap, the stronger the screening ability and the larger the processing capacity.
Material characteristics: particle size composition, humidity, viscosity, bulk density, etc. Dry, loose, and well flowing materials have a large processing capacity; For sticky and wet materials, the processing capacity may decrease, but it still has advantages compared to other screening machines.
Screen shaft speed and installation inclination angle: The speed and inclination angle together determine the forward speed of the material on the screen surface, directly affecting the processing capacity and screening efficiency. A certain inclination angle helps the material flow forward.

Application Field
Roller screens are suitable for handling materials with high flow rates, large blocks, high moisture content, and easy blockage.
Coal industry: Used for the preparation and screening of raw coal, dehydration and media removal of selected products, and screening of gangue.
Mining industry: used for particle size classification of various ores such as iron ore, limestone, granite, and pre screening before crushing.
Power industry: In coal-fired power plants, it is used to screen the incoming coal in the coal transportation system, directly feed qualified coal particles into the boiler, and send large coal blocks for crushing.
Metallurgical industry: used for screening sintered ore and coke.
Building materials industry: used for grading sand and gravel aggregates.
Waste disposal: In MSW recycling, it is used for coarse screening of waste, separating large debris and recyclable materials.
Applicable Materials
Roller screens are particularly suitable for materials with the following characteristics:
Sticky and wet materials: The principle of forced screening can effectively prevent clogging of sieve holes in raw coal with high moisture content, coal washing products, and clay ores.
Large block materials: It can handle materials with particle sizes up to 300–500 mm or even larger.
Materials with complex components, such as construction waste, household waste, can cope with the interference of flexible debris (such as plastic, wood) due to their strong structure and forced conveying capacity.
We are well aware that every production site faces unique challenges and demands, and there is no one size fits all solution. That is why GEP ECOTECH has never defined itself solely as a supplier of equipment. Based on our numerous successful project experiences accumulated globally, we promise to provide you with more than just one device. From equipment selection, process design to installation and commissioning, we will accompany you throughout the entire process to ensure that your investment receives the maximum return.
Contact our expert team immediately and let us create value for you with our professional experience.