

With the rapid development of social economy, people's quality of life is constantly improving, but the amount of domestic waste is also on the rise, so the treatment of domestic waste has become extremely critical. The treatment of domestic waste is based on environmental, health and resource pressures, and its management plan is based on complex specific policies, environments, times and technical levels. The domestic waste management system should be open, scientific and scalable. With the changes of the times, the characteristics of domestic waste and the continuous changes and improvements in demand, it needs to be implemented in stages, levels, regions and steps. The entire planning and management system must also keep pace with the times and continue to be revised and standardized. Although the domestic waste management industry has only been around for a short time, it is closely linked to people's livelihood. Any decision and planning is understandable, but it cannot be completely implemented in


In the realm of waste management, innovative technologies play a pivotal role in addressing the challenges posed by landfill waste accumulation. Our GDL Two Shaft Shredder stands at the forefront of waste processing solutions, offering efficient and sustainable grinding capabilities for landfill waste. This article delves into the process of grinding landfill waste with our GDL Two Shaft Shredder, highlighting its effectiveness and environmental benefits. Understanding Landfill WasteLandfill waste comprises a diverse array of materials, including organic matter, plastics, paper, textiles, and metals. Traditional disposal methods often result in inefficient waste management practices, leading to environmental degradation and resource depletion. Effective management of landfill waste is imperative to mitigate these impacts and promote a circular economy. The GDL Two Shaft ShredderOur GDL Two Shaft Shredder is a state-of-the-art waste processing solution designed to grind and shred various types of waste

The Role of Fine Shredders in Secondary Processing of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) management is a pressing global challenge, and effective waste processing technologies are essential for sustainable waste disposal. In recent years, fine shredders have emerged as valuable assets in the secondary processing of MSW. This article explores the significance of fine shredders in enhancing MSW processing efficiency and promoting resource recovery. Fine Shredders in MSW Processing: Size Reduction for Enhanced Sorting:Fine shredders play a crucial role in reducing the size of MSW materials, making them more manageable for subsequent sorting processes. By breaking down bulky items into smaller particles, these shredders facilitate the extraction of valuable recyclables and organic materials. Increased Surface Area for Biological Treatment:The fine shredding process increases the surface area of organic waste, promoting more effective biological treatment. This is particularly beneficial for


Recently, many customers have inquired whether it is possible to convert all MSW (Municipal Solid Waste) into high calorific value RDF? Here, it should be explained that in the field of MSW classification, many countries and regions currently do not reach the level of complete segmentation. MSW is still mixed with a large amount of kitchen waste, as well as low calorific value non combustible materials such as porcelain chips and stones. It is impossible to make such materials into high calorific value alternative fuels. Therefore, before MSW can be converted into alternative fuels, a series of shredding and screening equipment must be used to separate the non combustible materials inside, and the remaining combustible materials can be processed into high calorific alternative fuels RDF/SRF.The specific disposal process is as follows: MSW is transported to the MSW disposal center through specialized transportation vehicles, first dumped into the waste storage pit in the disposal center, and then collected

Recycling Treatment of Aged Waste
2023-10-19To recycle and dispose of aged waste, we first need to understand what kind of waste is called aged waste. Aged waste refers to the product of natural evolution after a long period of time after landfilling. After years of microbial decomposition and fermentation, the water content is usually high and the organic matter content is low. Simply put, aged waste is the waste excavated from landfills and is a product of the era of waste treatment. In the past, the main treatment method for domestic waste in China was sanitary landfill, so there are large landfill sites in various regions. In the past decade, the main treatment method for domestic waste has become incineration, so aged waste is all stored waste. Why should aged ;waste be excavated from landfills? There are mainly three reasons:① Extending the lifespan of landfills: saving landfill land and extending the lifespan of landfills. In addition, it is possible to obtain land resources and reuse landfills.② Anti seepage inspection and repair: After more


Facts: Municipal solid waste contains a large amount of high calorific value components, which will not be effectively utilized if the waste is directly incinerated or filled up. Through the existing thermal power plants, thermal power plants, cement plants for coupling power generation, co-disposal, combined with RDF fuel briquetting production technology, without landfill, without large investment in the construction of waste incineration power plant, urban household waste, industrial solid waste can be "harmless, reduction, resource, energy" comprehensive use of treatment applications. As MSW is incinerated directly as a solid fuel without treatment, the following main problems often exist.the organic matter in the waste is highly perishable, making transportation and storage more difficult.the waste is characterized by large fluctuations in composition and calorific value, high moisture and ash content, which can easily cause unstable combustionwaste often contains plastic, salt and other chlorine-


Shredding and Treatment of Bulky Wastes
2023-02-25Bulky waste disposal has always been a hot topic in urban environmental protection planning. Bulky waste disposal planning can be seen in many projects. At present, the disposal of bulky waste in the market has also gradually derived mature systems and methods, which have been well used around the world.From the perspective of the proportion of bulky waste, most of bulky waste is composed of wood, sponge, waste textile, plastic, metal and other materials, which have high recycling value, such as:1. Wood can be made into boards or crushed to make alternative fuels for incineration and power generation, so as to save coals;2. The sponge can be made of recycled cotton, other colored sponges and elastic materials;3. Waste textiles can be reprocessed into new textiles, or alcoholized by chemical methods and then polymerized and spun to produce polyester and other products; Waste textiles also have high calorific value, and can be used to produce alternative fuels for incineration power generation after shredding;


With the advancement of urbanization construction, the total amount of MSW/domestic waste generated in daily life is also increasing. The government has also invested a lot of energy in the treatment of domestic waste, and has also implemented policies and guidelines on the treatment of urban domestic waste. Many customers who have first contacted have many doubts about the treatment of domestic waste. Hereby, I will make a brief introduction about the treatment of domestic waste. At present, there are three main ways to treat domestic waste: landfill, compost and incineration. Landfill usually buries domestic waste directly underground to let the waste decompose naturally; The composting method requires the use of equipment to break the organic matter in the domestic garbage, and then degrade the organic matter to make compost; Incineration is the process of crushing and sorting domestic waste, or directly burning it for power generation, or making it into RDF combustion rods, which is basically heat energy


MSW Disposal Equipment for sale
2023-02-04MSW (municipal solid waste) disposal is divided into two forms: General pretreatment and resource utilization. For example, each waste transfer station only needs crushers and magnetic separators if it only provides waste pretreatment and transfer to the centralized Center for resource utilization. First, the domestic waste is crushed into smaller particles by the domestic waste shredder for convenient storage and transportation, and then the ferrous metals are magnetically separated, so that the processed materials can be packed and transported. It is efficient and convenient, and is very suitable for small and medium-sized waste treatment plants to pretreat the collected domestic waste and transfer it. If we want to make deep resource utilization of domestic waste, we need more sorting equipment. For example, domestic waste crushers are also divided into coarse crushers and fine crushers. After coarse crushing, roller screens are used for coarse screening to separate small pieces of heavy materials such as

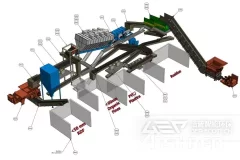
There is a lot of domestic waste produced in cities every day, which is increasing. Therefore, it is an urgent task to seek a way of recycling treatment of municipal solid waste. Converting municipal solid waste into waste derived fuel, namely RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel), is a mature waste treatment method in developed countries. RDF fuel has been widely used in the United States, Europe, Japan and South Korea to generate electricity or heat. How Does Municipal Solid Waste Become RDF?The production process of RDF is to first use sorting equipment to classify urban domestic waste, separate the recyclable parts according to different material properties, and then separate the waste plastics, waste paper scraps, wood chips, PVC and other combustible wastes from the waste through screening steps such as magnetic separation, air separation, non-ferrous metal screening and other steps, and then crush, dry and grind them into granular fuel. RDF is extruded and solidified into granules at high temperature. The RDF


At present, there are three main treatment methods for municipal solid waste(MSW): landfill, composting and incineration. Landfilling usually involves burying domestic waste directly underground to allow them to decompose naturally; The composting method requires the use of equipment to break the organic matter in the domestic waste, and then explain the organic matter to make compost; Incineration is the process of crushing and sorting domestic waste, or directly burning it for power generation, or making it into RDF combustion rod, which is basically thermal energy conversion. These three methods are widely used at present, and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Landfill occupies land resources, composting process is complex, and incineration needs to strengthen flue gas treatment. At present, there are more environmentally friendly new technologies, such as hydrogen production from domestic waste. No matter which of the above domestic waste treatment methods is used, it is for the purpose of


Waste Pre Shredder for MSW
2022-07-11You need a high-availability primary shredder for processing of municipal solid waste, whether for landfilling or making RDF. Shredder is the most common equipment in the field of solid waste management. Its function is to shred solid waste into small pieces for subsequent treatment. When dealing with municipal solid waste, the pre shredder can shred large pieces of waste into small pieces for easy sorting, at the same time, shredded combustible waste have a higher combustion efficiency. AIShred not only provides pre shredders for the treatment of municipal solid waste, but also provides total solutions, click here to view AIShred MSW solutions. How to get your tailored shredder information As you know, even the same model of shredder may use different motors or hydraulic drives, other supporting components may also be different, because the working conditions of each production line are different, so the shredders used in the production line are configured on a case-by-case basis. So how to get shredder


Size Reduction of Municipal Solid Waste
2022-06-16Size reduction is defined as operations or processes which reduce the size of influent materials through division into two or more subunits. Size reduction of municipal solid wastes (often called shredding, grinding, or pulverizing) is a new concept, and much of the technology has been borrowed from the mining and rock-crushing industry. Because solid waste is a heterogeneous mixture(unlike rock), much of the technology is not directly transferable; and size reduction of solid waste has not always been efficient; however,as more solid waste systems have been built, the technoloqy of solid waste size reduction has been sianificantly advanced. More than 2.01 billion tonnes of municipal solid waste are produced annually worldwide. Land areas suitable for land disposal near urban areas where the bulk of the solid waste is generated are becoming scarce and expensive. Open burning and open dumping have been outlawed in many areas because of pollution and health hazards. Incineration is becoming increasingly more

Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste
2022-06-06Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) contains organic as well as inorganic matter. The latent energy present in its organic fraction can be recovered for gainful utilisation through adoption of suitable Waste Processing and Treatment technologies. The recovery of energy from wastes also offers a few additional benefits as follows:The total quantity of waste gets reduced by nearly 60% to over 90%, depending upon the waste composition and the adopted technologyDemand for land, which is already scarce in cities, for landfilling is reducedThe cost of transportation of waste to far-away landfill sites also gets reduced proportionatelyNet reduction in environmental pollutionEnergy can be recovered from the organic fraction of waste (biodegradable as well as non-biodegradable) basically through two methods as follows:Thermo-chemical conversion: This process entails thermal de-composition of organic matter to produce either heat energy or fuel oil or gas;Bio-chemical conversion: This process is based on enzymatic

Municipal Solid Waste Recycling Methods
2022-06-04Biological or thermal treatment of municipal solid waste can result in recovery of useful products such as compost or energy.Biological ProcessesBiological treatment involves using micro-organisms to decompose the biodegradable components of waste. Two types of processes are used, namely:Aerobic processes: Windrow composting, aerated static pile composting and in-vessel composting; vermi-culture etc.Anaerobic processes: Low-solids anaerobic digestion (wet process), highsolids anaerobic digestion (dry process) and combined processesIn the aerobic process the utilisable product is compost. In the anaerobic process the utilisable product is methane gas (for energy recovery). Both processes have been used for waste processing in different countries – a majority of the biological treatment process adopted world-wide are aerobic composting; the use of anaerobic treatment has been more limited.Thermal ProcessesThermal treatment involves conversion of waste into gaseous, liquid and solid conversion products with

Municipal Solid Waste Twin Shaft Shredder
2022-05-11The AIShred GD12 shredder is a very economical, low-speed, twin-shaft shredder specially designed for the processing of household, industrial and commercial waste of coarse, medium and fine fractions, as well as for the processing of old wood. GD12 is great for processing of Municipal Solid Waste. Minimal operating costs with maximum performance, combined with the capabilities of intelligent technology, make the waste shredder an indispensable assistant. The Eco Drive delivers up to 50% energy savings compared to conventional electro-hydraulic drives. A feature of shredders is the ability to remotely monitor the operation and control via internet. By using the most advanced synchronous motors, the maximum level of efficiency is achieved, making the Eco Drive one of the most energy efficient drive systems on the market. Maintenance costs are kept to a minimum as belts, hydraulic pumps and shaft ends are not used on this model. If high performance and, accordingly, an increased rotor speed are required, it is


Municipal solid waste (MSW) is household, commercial, and / or institutional solid waste. They consist of everyday items such as paper, grass clippings, plastic bags, furniture, clothing, bottles, rubber, metals, food waste, paints and batteries. They are not only of domestic origin, but also commercial (offices, retail and wholesale, restaurants), institutional (libraries, schools, hospitals, prisons) and industrial (packaging and administration). Most of them are classified as not dangerous. As part of their solid waste management plan, almost all countries are promoting source reduction, recycling and composting to reduce landfill disposal. Several countries have also adopted specific measures for the disposal of certain materials: leaves, grass clippings, yard waste, office waste and computer paper, newsprint, cardboard and corrugated cardboard, glass, plastic, aluminum and steel containers are prohibited in disposal plants. Many plants burn municipal solid waste at high temperatures not only to reduce



